Why is Laser cutting so important to fabrication?
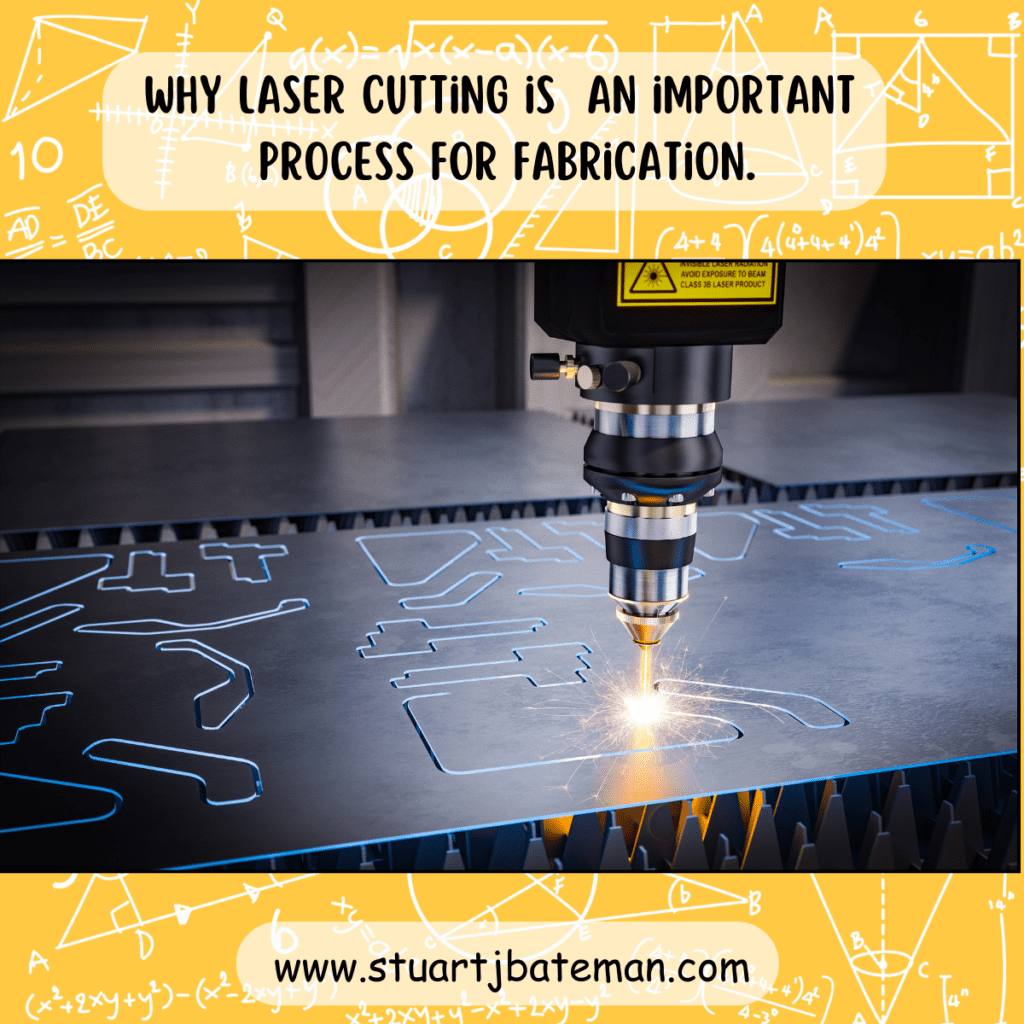
Some background to Laser cutting.
Manufacturing through laser cutting has been a pivotal process since the 1970s, offering crucial advantages in fabrication.
This method harnesses high-powered CO2 emitters to generate a beam capable of penetrating sheet metal. Essentially, the laser heats a specific area of the steel to a molten state while compressed air is simultaneously blown onto the spot. This prevents the heat from affecting the surrounding steel, except within the beam’s width.
The resulting cut leaves behind a distinctive ‘kerf’ edge, characterized by a wavily patterned crust along the steel’s perimeter.

Waste material is collected at the base of the machine for later removal.
At Stannah, we utilized lasers with capacities of up to 5KW, capable of cutting through sheets up to 8mm thick. These cut parts were subsequently welded together to construct the chassis and other components for our stairlifts.
The benefits of laser cutting are many:
- Speed: Laser cutting offers rapid cutting capabilities.
- Tolerances: Achieving tolerances of +/-0.2mm (though newer models likely offer even tighter precision).
- Efficiency: Faster manufacturing times compared to machining from solid blocks.
- Complexity: Laser cutting facilitates the creation of intricate shapes, akin to drawing on a piece of paper.
- Automation: Laser cutting machines can be integrated with auto loaders for lights-out operation.
- Workholding: Utilization of copper slat beds for easy work holding, albeit with some challenges in cleaning.
- Reduced Warping: Laser cutting minimizes material warping during the process.
- Versatility: Ability to cut materials that pose challenges for traditional methods, such as glass, wood, and plastic.
Cons.
However, it’s essential to acknowledge the drawbacks that come with this advanced technology:
- Cost: The initial investment in laser cutting equipment can be substantial, making it less accessible for smaller businesses and startups.
- Material Limitations: Laser cutting is primarily suited for thin to medium-thickness materials, limiting its applicability for thicker materials or highly reflective surfaces.
- Edge Quality: While laser cutting produces clean and precise edges, it may result in heat-affected zones, affecting the material’s structural integrity and surface finish.
- Maintenance Requirements: Laser cutting machines require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and reliability, adding to operational costs and downtime.
- Safety Concerns: The use of high-powered lasers poses safety risks for operators, necessitating strict adherence to safety protocols and protective measures.
Different types and manufacturers for Laser cutting machines.
While Stannah employed Trumpf laser cutters, it’s worth noting that various manufacturers and types of lasers exist in the market, each with its own strengths and applications within manufacturing.
Another way to manufacture parts.
In addition to direct cutting, parts can also be produced by stacking flat patterns and welding them together. This process involves cutting individual components from flat sheets using laser cutting technology, stacking them to form the desired shape or structure, and then welding them together to create a solid assembly. This method allows for greater flexibility and customization in part design, as well as the integration of additional features or components. Once assembled, the parts can be further machined to add additional features or refine the final dimensions, ensuring optimal fit and functionality.
My interest
Of particular interest are combination punch lasers, which enable the creation of 3D forms and integration of structural fixings like threads, addressing a limitation of flat-pattern lasers.
By leveraging the capabilities of laser cutting and advanced manufacturing techniques, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, flexibility, and precision in their production processes, ultimately driving innovation and competitiveness in today’s dynamic market.
This overview encapsulates my experiences with laser cutting machines. I’m keen to hear about your own encounters and insights in this field.
Websites that have information on Laser cutting:
https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/job-knowledge/cutting-processes-laser-cutting-052
https://www.instructables.com/Laser-Cutting-Basics/
YouTube videos:
How does laser cutting work? Basics explained
How does the CNC Fiber laser cutting machine work? – Factories



What are your thoughts? Have I covered everything or is there more you know and would like to share?
I’m always learning and improving this site and my blogs, so please feel free to get in touch with me via LinkedIn or this site to discuss any topics I have covered.
If you’re having trouble finding ways to progress check out these sites filled with free learning tools:


Discover more from The Chartered Engineer
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.